Comparative Adjectives
- Comparative adjectives compare differences between two objects or people.
- We form comparative adjectives in different ways depending on the number of syllables.
- We use "than" to show the comparison.
- Common patterns with comparative adjectives: Comparative adjective + "and" + comparative adjective to show gradual changes, and "the" + comparative adjective + subject + verb, "the" + comparative adjective + subject + verb.
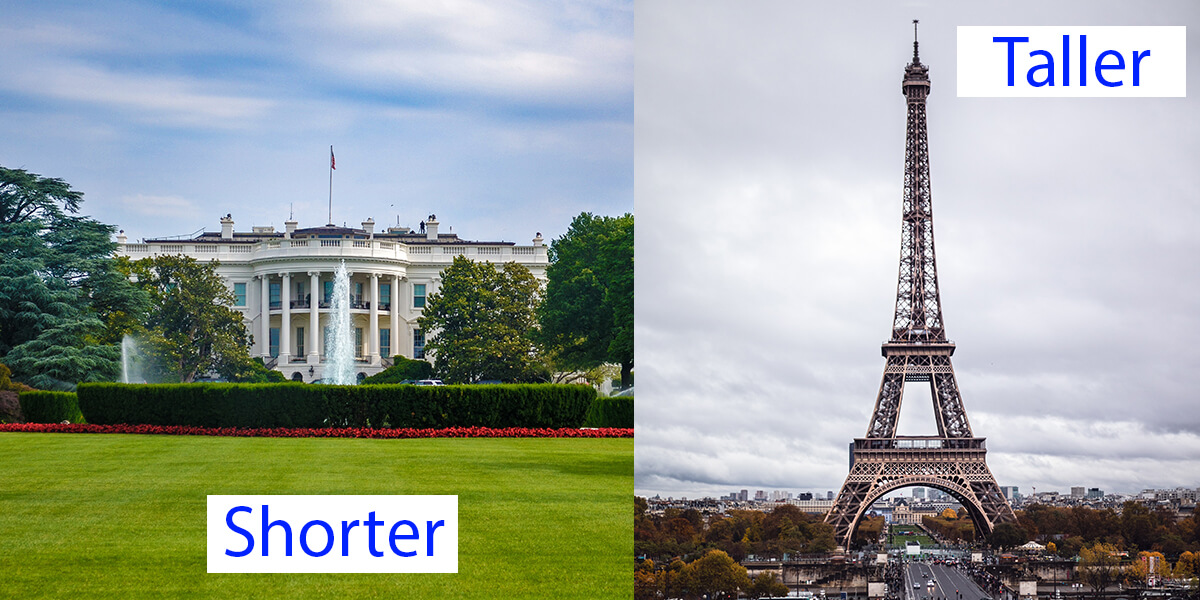
Comparative adjectives help us compare two things. We use them to show how one thing is different from another. Let's learn how to form and use them.
Here's an example sentence: "The Eiffel Tower is taller than the White House."

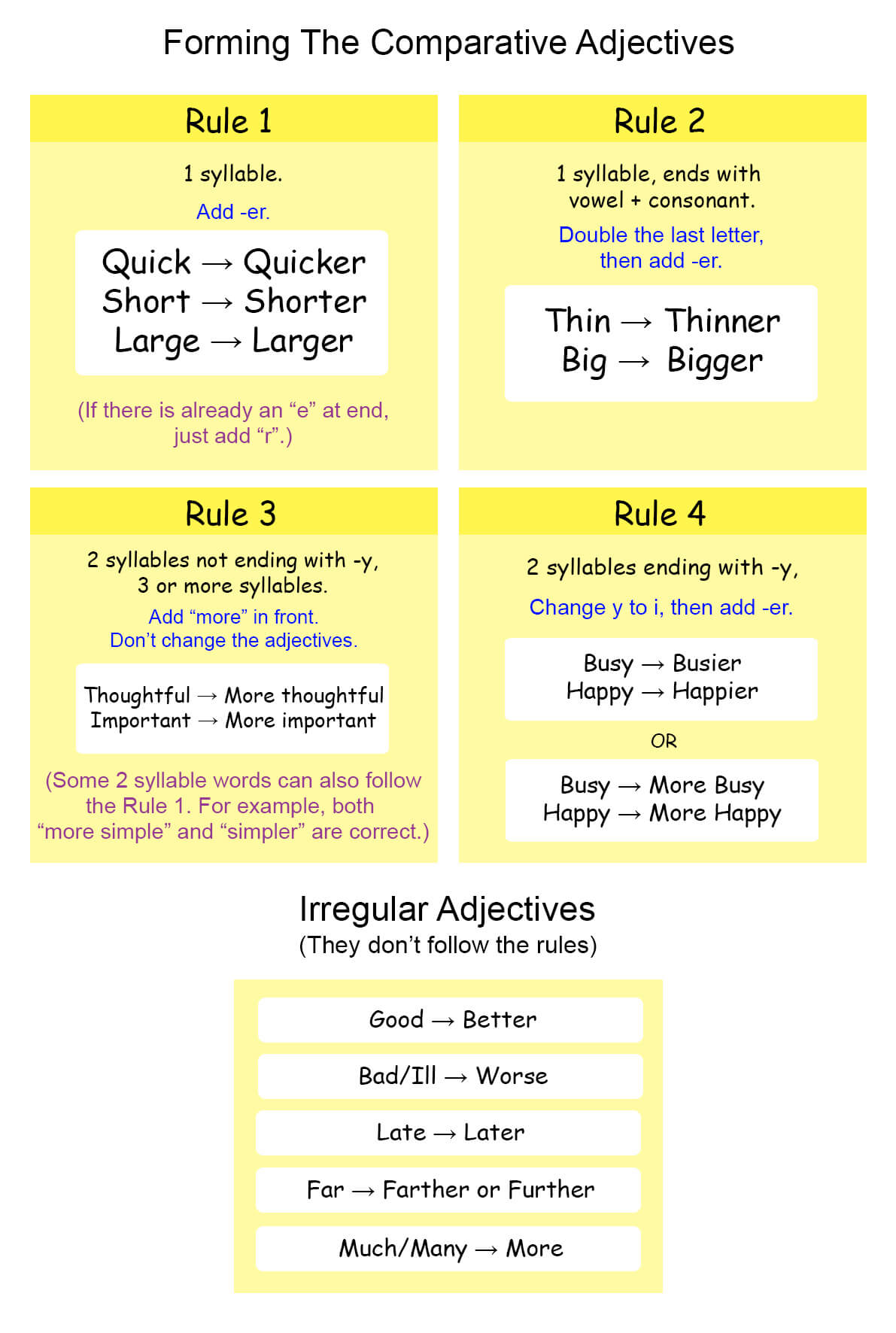
Forming Comparative Adjectives
We form comparative adjectives based on the number of syllables in the adjective. Here are the rules:
Rule 1: For one-syllable adjectives, add -er.
Examples: quick → quicker, short → shorter, large → larger
Rule 2: For one-syllable adjectives ending in a vowel + consonant, double the last letter and add -er.
Examples: thin → thinner, big → bigger
Rule 3: For adjectives with two syllables not ending in -y, or adjectives with three or more syllables, add "more" before the adjective.
Examples: thoughtful → more thoughtful, important → more important
Rule 4: For two-syllable adjectives ending in -y, change the -y to -i and add -er.
Examples: busy → busier, happy → happier
Some adjectives are irregular and don't follow these rules. Here are a few:
Good → better, bad → worse, far → farther/further
Basic Grammar of Comparative Adjectives
You can use a comparative adjective just like any other adjectives.
Example: "I have a bigger house now."
If you want to compare two things, use the preposition "than".
Grammar Rule: Subject + be verb + comparative adjective + "than" + object.
Examples:
-
My friend is taller than me.
Subject ("My friend") + be verb ("is") + comparative adjective ("taller") + than + object ("me").
-
I have a bigger house than you.
Subject ("I") + verb ("have") + article ("a") + comparative adjective ("bigger") + object ("house") + than + object ("you").
Common Patterns with Comparative Adjectives
Pattern 1: Comparative adjective + "and" + comparative adjective
This pattern shows that something is continuing to change.
Examples:
-
The bubble is becoming bigger and bigger.
The bubble keeps getting bigger.
-
The weather is getting colder and colder.
The weather keeps getting colder.
Pattern 2: "The" + comparative adjective + subject + verb, "the" + comparative adjective + subject + verb
This pattern shows that two things change together.
Examples:
-
The higher the price of the stock got, the more people bought the stock.
As the stock price increased, more people bought it.
-
The more you study, the better your grades will be.
Studying more improves your grades.
Comparative adjectives help us describe differences and changes. Practice using these patterns to make your English more precise and interesting!
Practice this topic with the AI English Tutor
AI English Tutor will teach you the grammar and practice it with you in a conversation format. Plus, 100+ practice questions on this topic to cement your understanding.
Try ALULA for free on your phone or tablet








Do you have any questions about this lesson? Ask in the comment section, below.