Verb + To-infinitive
- The to-infinitive form of a verb is used after certain verbs to express purpose, intention, desire, or a future action.
- Basic usage includes verbs such as like, want, need, and would like.
- Other usage includes verbs like promise, threaten, refuse, and agree.
- You can place a direct object after the main verb to express who receives the action."
The to-infinitive form is a very useful part of English grammar. We can express reasons, purposes, and intentions with clarity. An "infinitive" is the base form of a verb. "To-infinitive" is "to" + a verb in its base form. Examples are "to eat", "to get", and "to use". Starting from the basics, we'll explore how the to-infinitive interacts with both common and more complex verbs.
Basic Uses of To-Infinitive
The to-infinitive often follows verbs that express desire, need, or preference. Examples are "like", "want", "need", "love", and "hate". This construction helps to clarify the action that the subject wants, needs, or prefers to do.
Examples: "like to play", "want to eat", "need to sleep", "love to read", and "hate to say".
In the case of "like to play", "like" is a verb and "to play" is a to-infinitive. A to-infinitive is "to" + an infinitive (a verb in its base form).
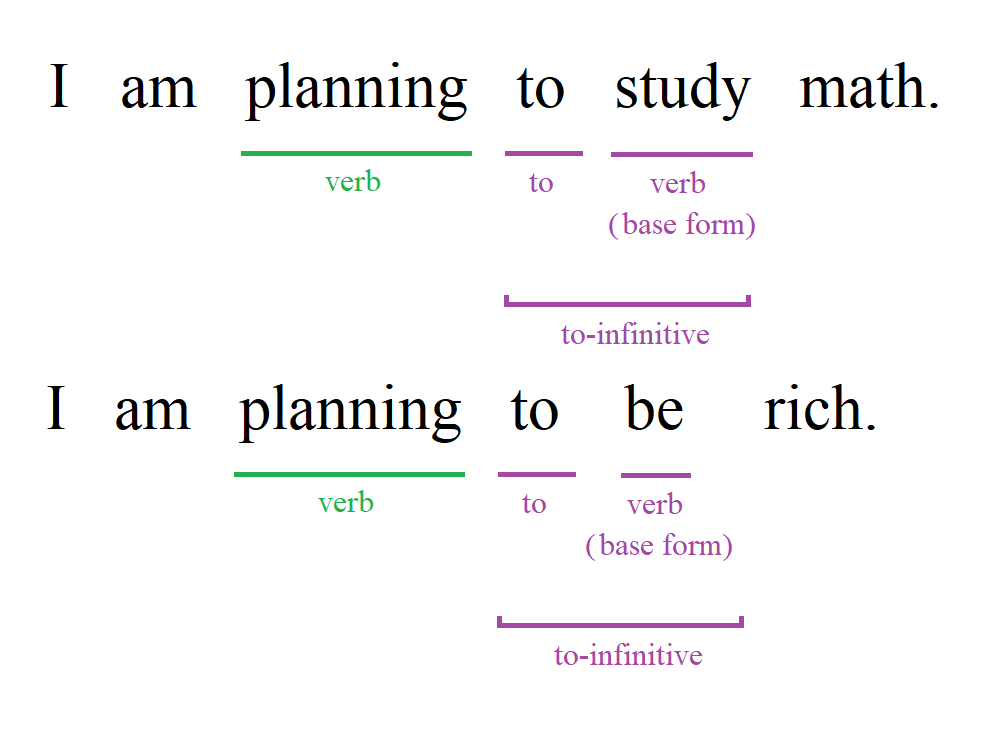
Examples:
-
I want to learn English.
Subject ("I") + verb ("want") + to-infinitive ("to learn") + object ("English").
-
She needs to go to the store.
Subject ("She") + verb ("needs") + to-infinitive ("to go") + prepositional phrase ("to the store").
Other Verbs Followed by To-Infinitive
Other verbs that can go before a to-infinitive includes verbs for saying something. These include "promise", "threaten", "refuse", and "agree". The to-infinitive helps to express actions related to commitments, warnings, denials, and consents.
Examples: "promise to work", "threaten to quit", "refuse to come", and "agree to pay".
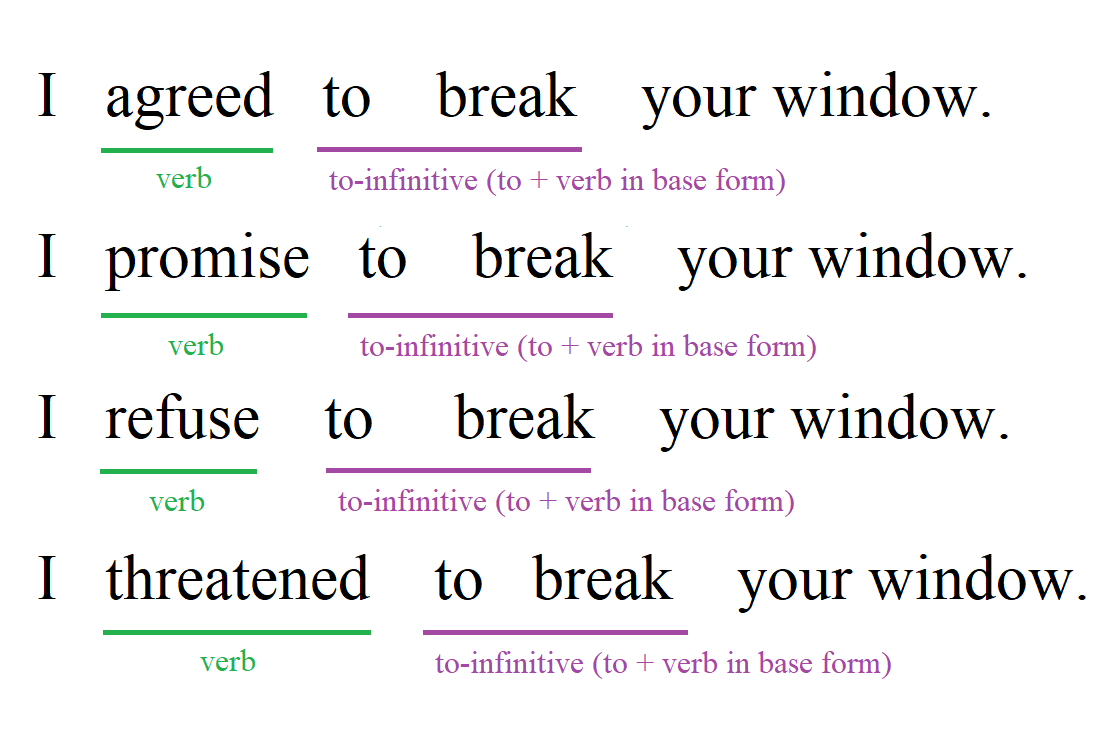
Examples:
-
He promised to help her.
Subject ("He") + verb ("promised") + to-infinitive ("to help") + object ("her").
-
She refused to accept the offer.
Subject ("She") + verb ("refused") + to-infinitive ("to accept") + object ("the offer").
Direct Object with To-Infinitive
You can put a direct object before the to-infinitive for some verbs.
Grammar rule: Subject + Verb + Direct Object + To-Infinitive.
Example: "I want Ted to come to my party."
The direct object receives the action of the to-infinitive. It provides clear information about who is to perform the action or who is affected by it.
Examples:
-
I asked him to call me.
Subject ("I") + verb ("asked") + direct object ("him") + to-infinitive ("to call") + object ("me").
-
She wants her team to win.
Subject ("She") + verb ("wants") + direct object ("her team") + to-infinitive ("to win").
Practice this topic with the AI English Tutor
AI English Tutor will teach you the grammar and practice it with you in a conversation format. Plus, 100+ practice questions on this topic to cement your understanding.
Try ALULA for free on your phone or tablet








Do you have any questions about this lesson? Ask in the comment section, below.