Present Continuous Tense
- The present continuous tense is used to talk about actions happening now or around the moment of speaking.
- Its negative form is used to talk about actions that are not happening now.
- The structure for the present continuous tense is: Subject + be verb + verb-ing (gerund) + (optional object). For negative sentences, add 'not' after the be verb.
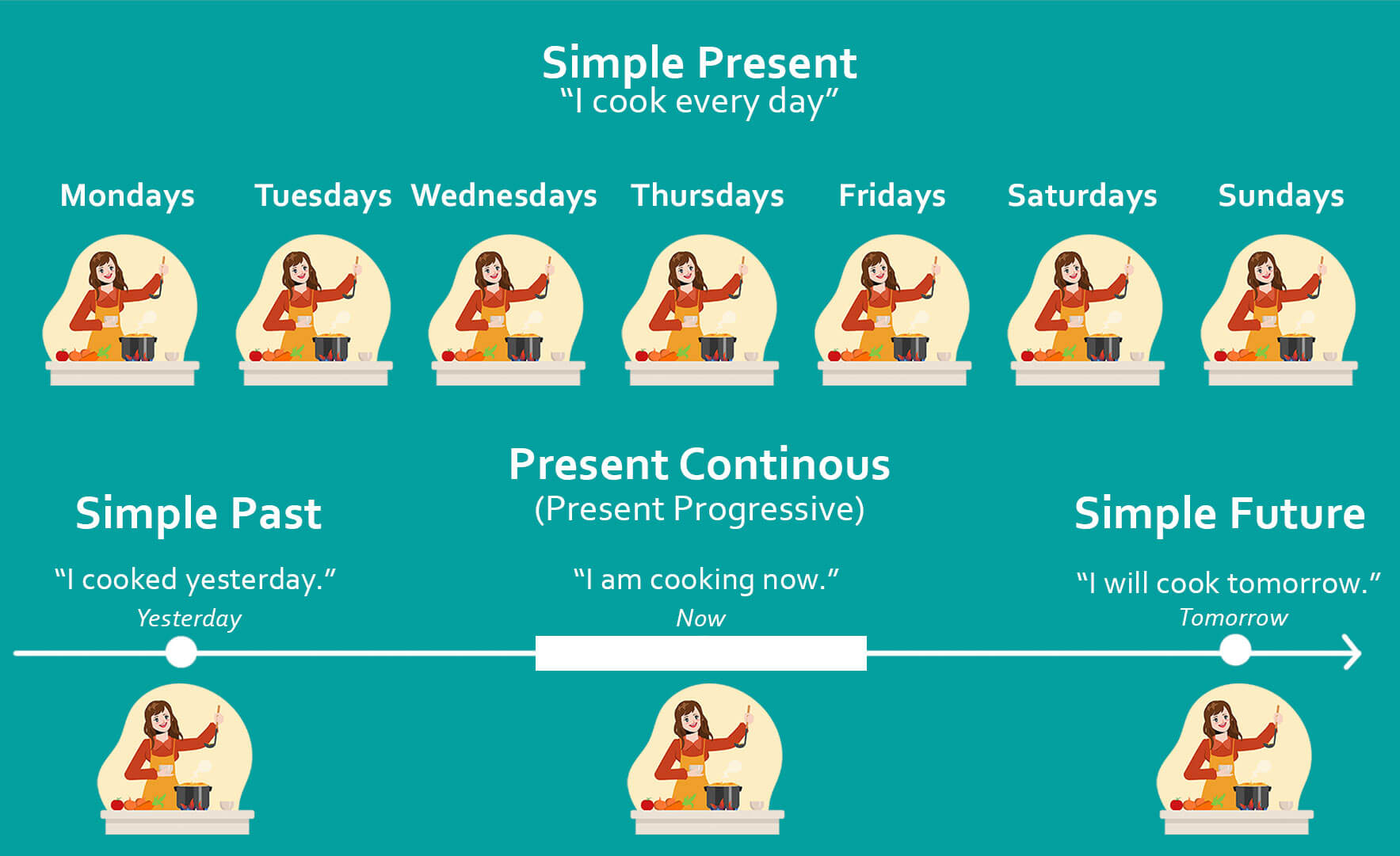
The present continuous tense is crucial in English for discussing actions occurring at the present moment or ongoing actions.
Simple present tense is used to describe your habits. Present continuous tense is used to describe what you are doing at the moment. An action in present continuous tense starts a little bit before the present moment, continues in the present moment, and ends a bit after the present moment.
Gerunds
Gerunds are the -ing form of verbs used as nouns. In the present continuous tense, we use the gerund form to describe ongoing actions.
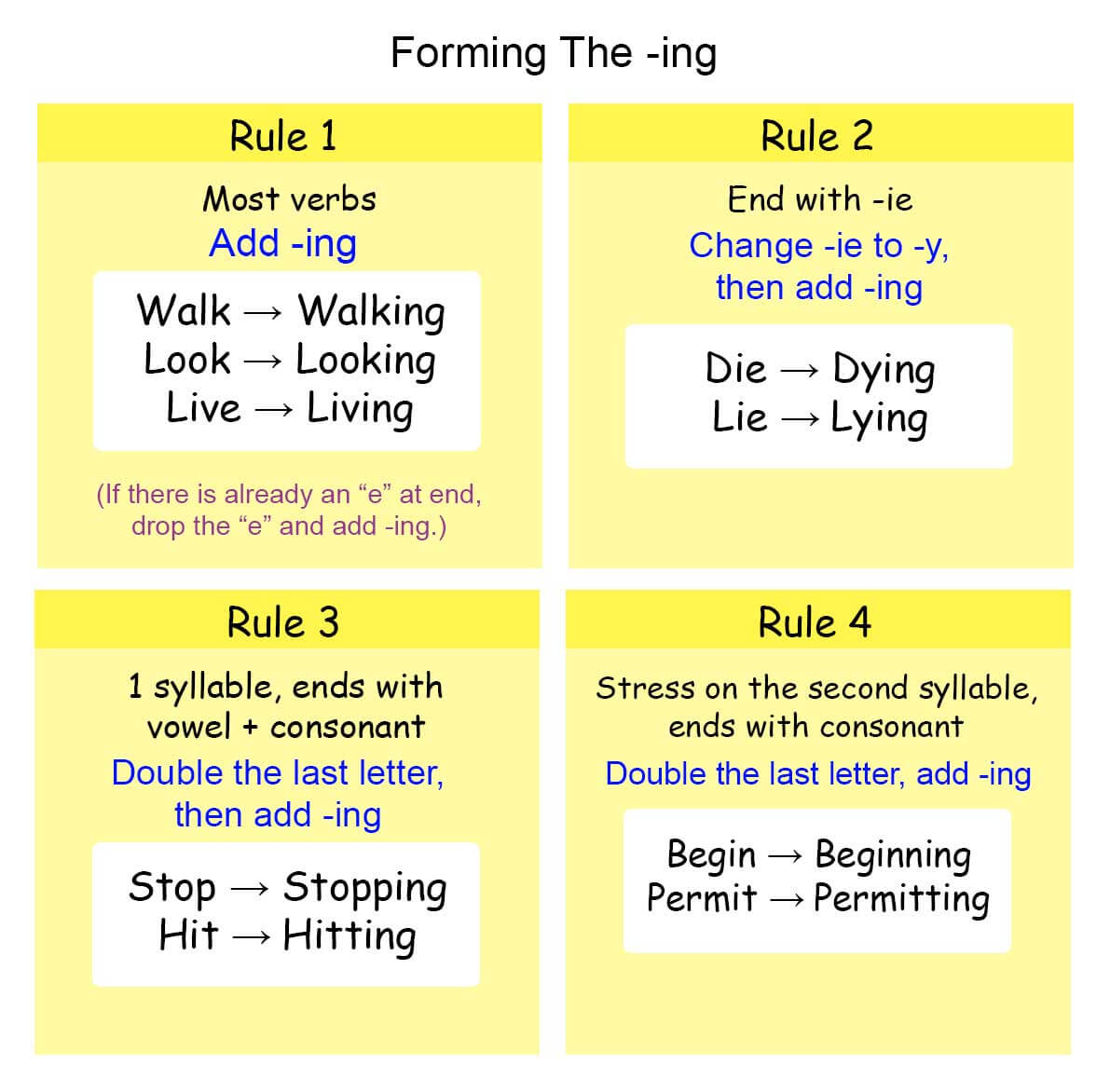
To form a gerund, simply add -ing to the base form of a verb. For verbs ending in -e, drop the -e before adding -ing (e.g., "make" becomes "making"). If the verb ends in a consonant + -ie, change -ie to -y and add -ing (e.g., "lie" becomes "lying").
Forming the Present Continuous Tense
Grammar Rule: Subject + be verb (am/is/are) + verb-ing (gerund) + (optional object).
Examples:
-
I am reading a book.
Subject ("I") + be verb ("am") + verb-ing ("reading") + object ("a book").
-
They are playing football.
Subject ("They") + be verb ("are") + verb-ing ("playing") + object ("football").
Negative Form of the Present Continuous Tense
Grammar Rule: Subject + be verb (am/is/are) + not + verb-ing (gerund) + (optional object).
Examples:
-
She is not watching TV.
Subject ("She") + be verb ("is") + not + verb-ing ("watching") + object ("TV").
-
We are not cooking dinner.
Subject ("We") + be verb ("are") + not + verb-ing ("cooking") + object ("dinner").
Remember, the present continuous tense does not pair with stative verbs, which describe states rather than actions. Hence, we say 'I know' instead of 'I am knowing'.
Practicing the formation of sentences in the present continuous tense, both affirmative and negative, helps you discuss ongoing or current actions more fluently in everyday conversations.
Practice this topic with the AI English Tutor
AI English Tutor will teach you the grammar and practice it with you in a conversation format. Plus, 100+ practice questions on this topic to cement your understanding.
Try ALULA for free on your phone or tablet








Do you have any questions about this lesson? Ask in the comment section, below.