Present Perfect Tense
- The present perfect tense is used to describe actions that happened at an unspecified time or that began in the past and continue in the present.
- To form the present perfect tense, use "have" or "has" followed by the past participle of the verb.
- The past participle form of a verb usually ends in -ed for regular verbs, but irregular verbs have unique past participle forms.
- Negative sentences in the present perfect are formed by adding "not" after "have" or "has".
The present perfect tense is a fascinating aspect of English grammar, blending past actions with present relevance. This lesson delves into how to use it effectively, including forming negative sentences and understanding past participles.
What is Present Perfect Tense?
The present perfect tense describes actions or events that have occurred at an unspecified time before now. The exact time is not important. It can also express actions that started in the past and are still happening or have a current impact.
For example, if you did your homework some time in the past, and if that's the reason you are relaxed now, you can use the present perfect and say, "I have finished my homework."
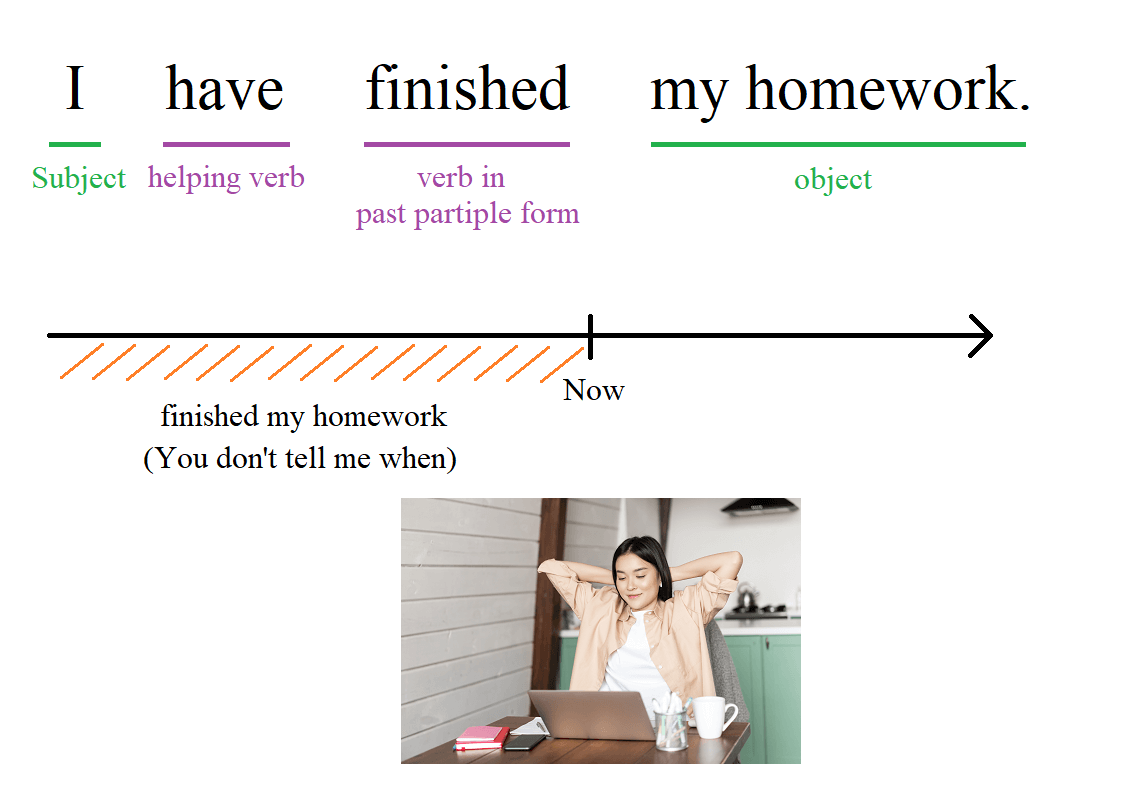
Forming the Present Perfect Tense
To form a sentence in the present perfect tense, use this grammar rule:
Grammar Rule: Subject + "have"/"has" + past participle of verb.
(Use "have" with "I", "you", "we", and "they". Use "has" with "he", "she", and "it".)
Every verb has 3 forms: Base form, Past tense form, and Past participle form.
Example: "eat" - base form. "ate" - past tense form, "eaten" - past participle form.
Past participle forms are used to construct the present perfect tense. For regular verbs, simply add -ed to the base form. However, irregular verbs vary, so they must be memorized.
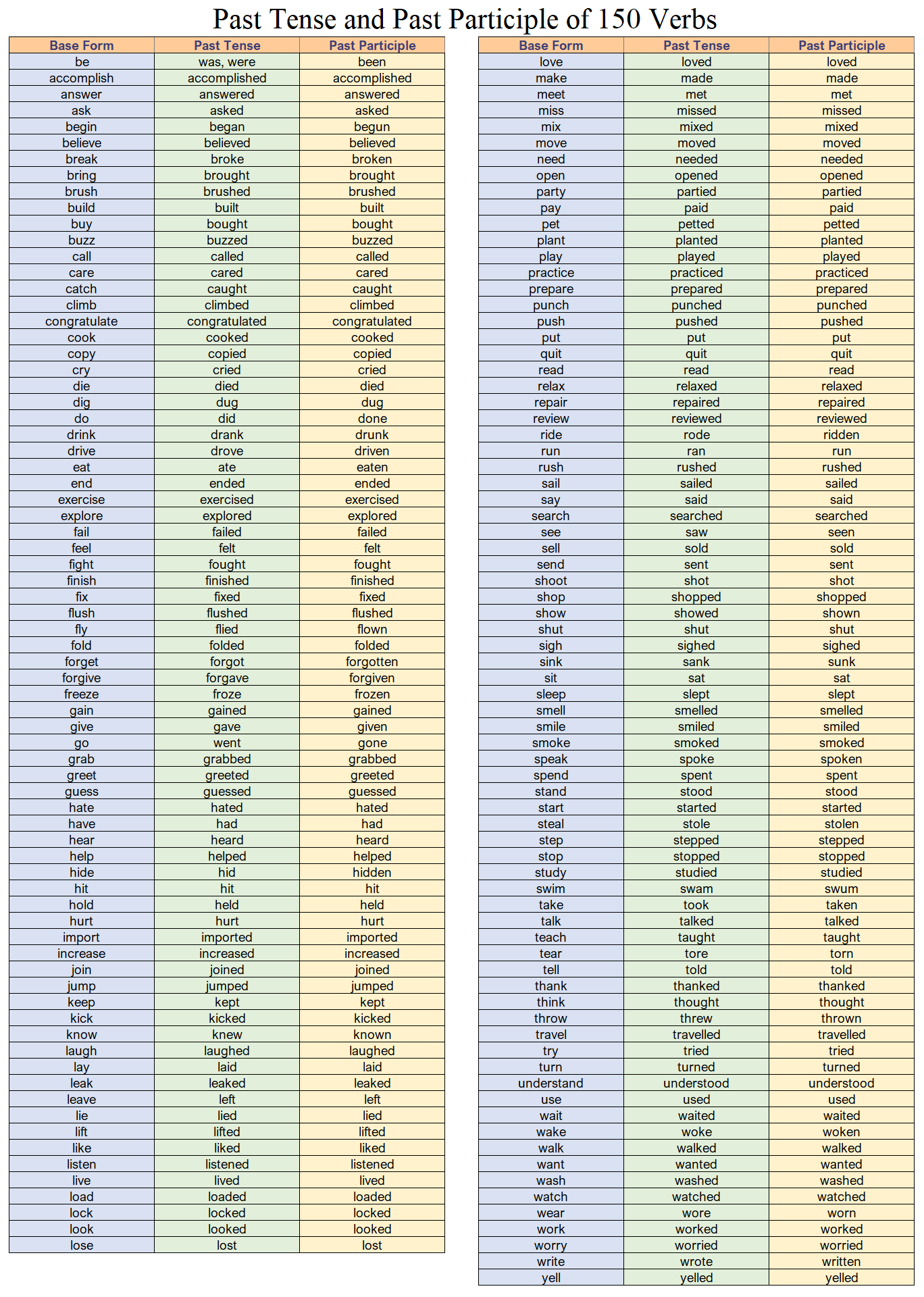
Examples:
-
I have visited Paris.
Subject ("I") + "have" + past participle form of verb ("visited") + object ("Paris").
-
She has cooked dinner.
Subject ("She") + "has" + past participle form of verb ("cooked") + object ("dinner").
Forming Negative Sentences in Present Perfect Tense
To make a sentence negative in the present perfect tense, insert "not" between "have" or "has" and the past participle.
Grammar Rule: Subject + "have"/"has" + "not" + past participle of verb.
(You can use the contraction "haven't" or "hasn't" in place of "have not" and "has not".)
Examples:
-
They have not finished their work.
Subject ("They") + have + not + past participle form of verb ("finished") + object ("their work").
-
He hasn't seen the movie yet.
Subject ("He") + "hasn't" ("has not") + past participle form of verb ("seen") + object ("the movie").
Pratiquez ce sujet avec le AI English Tutor
AI English Tutor vous apprendra la grammaire et la pratiquera avec vous sous forme de conversation. De plus, plus de 100 questions pratiques sur ce sujet pour consolider votre compréhension.
Essayez ALULA gratuitement sur votre téléphone ou votre tablette







Avez-vous des questions sur cette leçon ? Posez-les dans la section des commentaires, ci-dessous.